Inventory management is a challenge for most retailers. Inaccurate stock levels can lead to customer complaints, manual stock checks can take hours, and items are often lost. Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology can solve all of these problems.
At first glance, RFID technology might sound like an overly technical solution that’s only used by big brands. But more small retailers are leaning into RFID inventory management systems. There’s a small learning curve associated with the technology—one that pays off in the long run when you take advantage of the benefits RFID has to offer.
If you’re unsure where to start, this guide to RFID inventory management shares how the technology works, with a step-by-step guide on how to implement it for your own store.
Table of contents
What is RFID inventory management?
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) is a type of technology that retailers can use to manage their inventory. It works by using RFID tags which contain electronically stored information, such as stock keeping unit (SKU) numbers, product prices, and stock levels. The retailer can then use an RFID reader to find this data quickly and efficiently.
RFID vs. barcodes
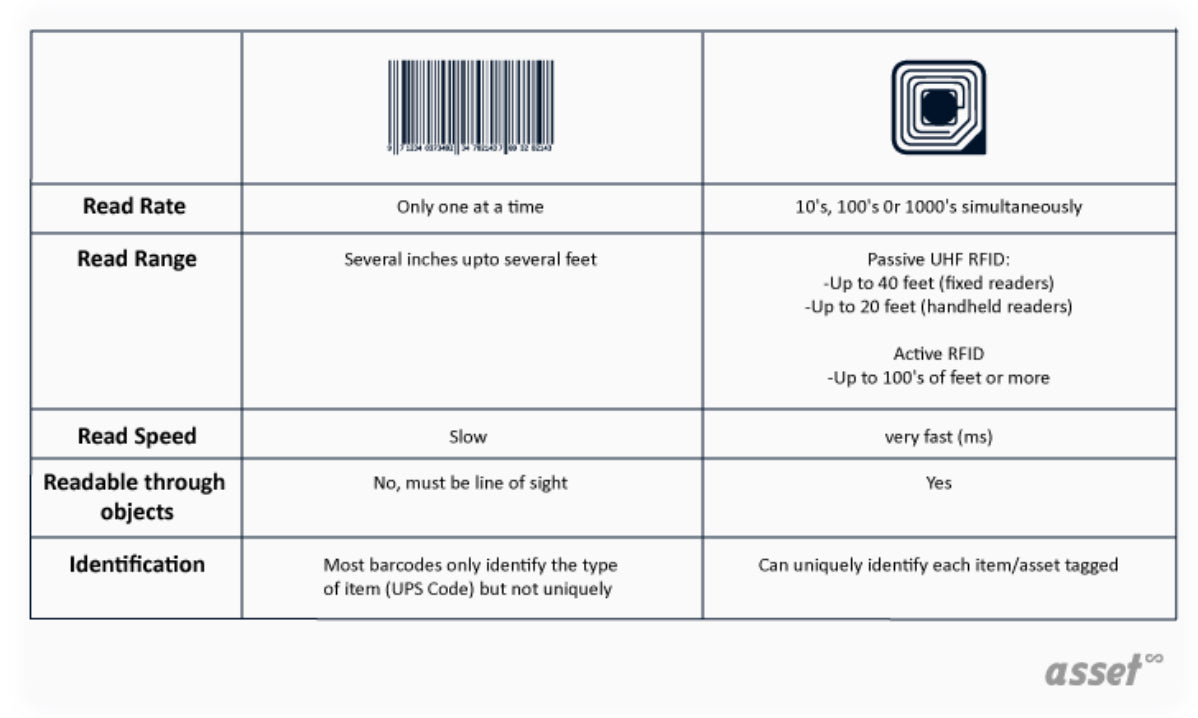
An RFID tag works similarly to a barcode in the sense that it helps retailers find product information quickly. The main difference between the two is that a barcode reader needs a direct line of sight with the product. This can be problematic if barcode labels fall off, or the lines on a barcode are damaged (like if a splash of water makes the ink run).
Active RFID tags, however, are more durable than barcodes because an RFID scanner doesn’t need a direct line of sight to the tag. Simply place the scanner in close proximity to the tag to see product information on the reader’s screen.
How does RFID inventory management work?
RFID technology works by storing data on a small tag that’s placed on a product, such as a tag on a piece of clothing. This tag has a unique identifier that’s specific to that item. It stores information about the product, such as:
- SKU numbers
- Inventory levels
- Product names and descriptions
- Prices, including any discounts or promotions
- Supply chain history, such as the item’s origin or supplier
Retailers then use RFID scanners to monitor where inventory is (without manually counting). This increases inventory visibility and gives them real-time information on where their products are.
For example, a small business owner might have an RFID scanner on the door to their brick-and-mortar store. The scanner syncs with their point of sale (POS) system to keep track of which products have been paid for. If someone exits your store and your POS hasn’t recognized the product as being sold, the RFID scanner will sound an alarm so you can prevent loss and deter thieves.
Benefits of an RFID inventory system
Improve inventory accuracy
Accuracy is key when monitoring stock levels. The last thing you want is to promise a customer they can have a product, only for it to be out of stock. Making them wait a few days for new stock could drive them toward a competitor.
Studies have found that retailers using RFID tags have up to 13% more accurate stock levels than those that do manual counts. Why? Because when an RFID scanner can detect information about a product, it reduces human errors associated with data entry, miscounts, or missed barcode label scans.
RFID systems can also scan multiple items at once. This significantly reduces the likelihood of missing items during manual inventory checks.
📦 INVENTORY TIP: Set reorder points in Shopify Admin to get low-stock notifications and ensure you have enough lead time to replenish inventory of a product before quantities reach zero.
Faster order fulfillment
If you’re using your retail store as a mini distribution center, your stock room might feel like an unorganized mess. RFID technology helps you locate products in the busiest of warehouses because you can use scanners to detect where specific items are.
You can also automate processes like shipment confirmation with RFID tags. Before shipping the order to your customer, run all boxes through the scanner to check that they match the packing slip.
Loss prevention
Theft costs retailers an estimated $100 billion per year. But with RFID tags, you can deter thieves from shoplifting in your store. If the scanner at your door detects a product that hasn’t yet been rung up in your POS software, an alarm will sound to alert you of the stolen goods.
You can also use an RFID system to verify that returned products are genuine. Return fraud is a common issue that happens when people return stolen or counterfeit products in exchange for a full refund. Your products will have a unique RFID tag that can show the item’s history, reducing the likelihood of handing out refunds for bogus inventory.
Plus, by accurate inventory tracking throughout the supply chain and within your stores, you’ll be able to identify discrepancies between expected and actual inventory counts much faster than manual counting would allow. Discrepancies may indicate theft or shrinkage—two major problems that can be costly if you don’t spot them quickly.
Disadvantages of RFID stock management
Extra equipment required
Compared to traditional barcode systems, the process of installing and configuring RFID equipment can be more complex. You’ll need specific RFID readers, tags, antennas, and software to get your system up and running.
RFID technology is also expensive and requires ongoing maintenance, which some retailers simply can’t warrant.
Data security concerns
Active RFID tags can be read remotely by anyone with an RFID reader. If someone enters your store with their own device, they can read data that you’ve stored inside the chip. Avoid adding any sensitive information on your tags that you don’t want to risk landing in the wrong hands, such as customer data or supplier contracts.
Compatibility issues
Not all RFID technology uses exactly the same software. Different scanners pick up different frequencies. You might need to change your tags (or your scanners) if manufacturers use different ones.
How to build an RFID inventory management system
Most retailers find that the advantages of using RFID for effective inventory management outweigh the negatives. If you agree, here’s how you can build your own system.
1. Buy RFID tags
The first step is to create RFID tags that store product data. Outsourcing is the easiest way to do this since the process of actually creating and programming a tag requires special expertise. For most retailers, the small cost of buying pre-made tags outweighs the priority of learning how to make them.
2. Choose an RFID reader or antenna
An RFID reader is the device you’ll use to scan tags. You can pick these up for around $30. Just make sure that yours integrates with your ecommerce platform or inventory management system.
3. Add your product data
Use the RFID antenna to scan your product tags. Upload the information you want to store on the tag, such as the product name, its SKU number, and price. Repeat these inventory processes for each product, then place the tag on the product. You can do this by either using an adhesive RFID label, a hang tag, or sewing it in.
4. Integrate it with your inventory management software
Once you’ve tagged all of your stock, integrate your inventory management software. This will ensure that your beginning inventory is accurate, and that when an RFID tag is detected, the levels in your IMS are accurate.
5. Test your tags
Think about how you’ll use your RFID tags and do some test runs to check that they’re working as expected. For example, you might:
- Try to exit your store with a product off the shelf to see if the RFID antenna will recognize it hasn’t been scanned at the checkout.
- Scan an RFID tag to see how many items you have in stock, then compare this against your manual stock check to confirm it is accurate.
- Set alerts to monitor product displays. If you’ve specified that five units should be on show at all times, does the RFID technology alert you when you only have four?
Manage inventory with RFID tags
RFID inventory systems are popular because they help retailers locate product information quickly, monitor inventory levels, and minimize shrinkage.
If you’re unsure of whether you should be using RFID for inventory management, launch a pilot scheme. Buy a small quantity of RFID tags and a small scanner, and choose which products you’d like to monitor the inventory of. You’ll soon find the right inventory management method for your retail business.





